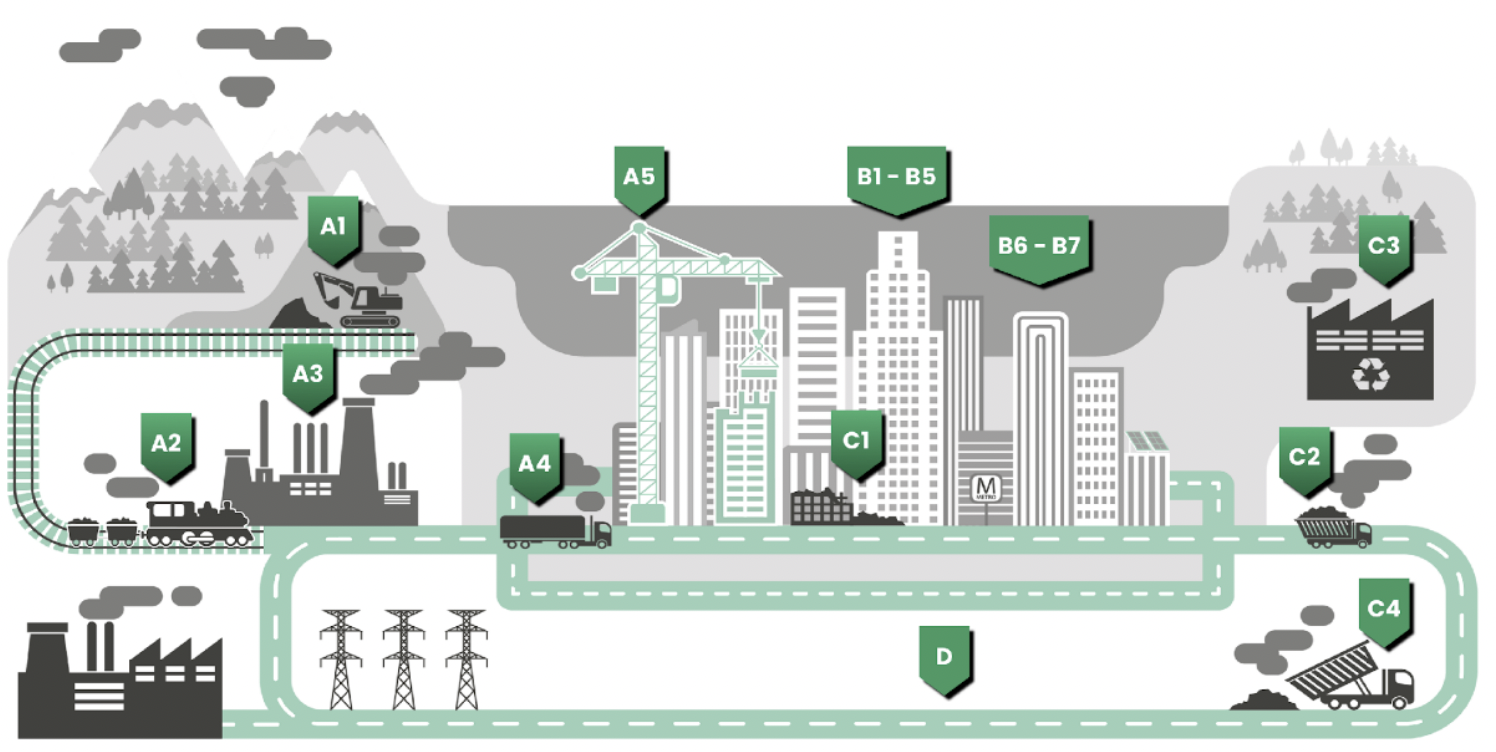
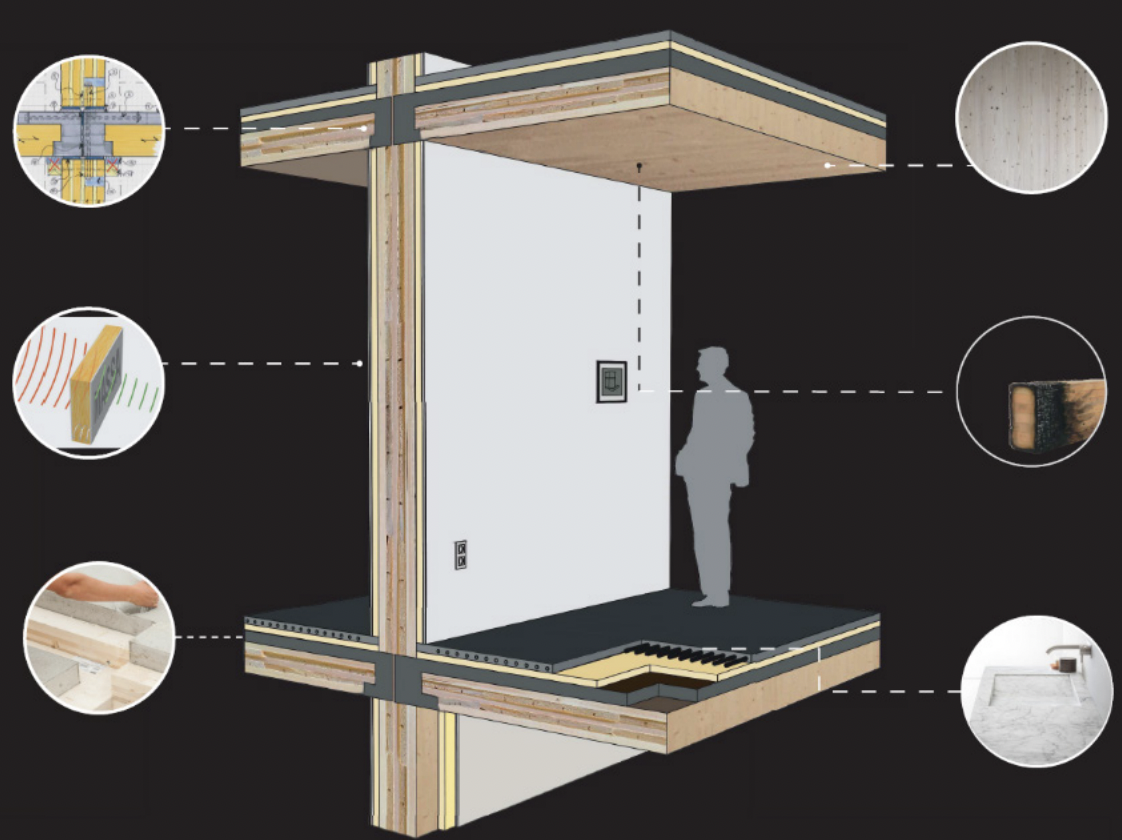
Overview
From the production of original research to the influence of multi-level policies, CNCA’s strategic focus is people-centered and spans the ecosystem of cities and industry stakeholders to dramatically decarbonize the built environment across geographies.